
NEWS
Deer smart - Research Institute
The era of industry and manufacturing: Retrospect, reflection and prospect
(Part I)
When we talk about the "industrial revolution," we may conjure up images of the roaring steam engine, or we may conjure up images of more contemporary elements such as assembly lines, automation equipment, and digital factories. In fact, the evolution of industry is never isolated, it involves not only social and economic changes, but also breakthroughs in science and technology and management ideas. From the beginning of mechanization in the 18th century, to the informationization of the 20th century, to the digitalization and intelligence of the 21st century, we are in a wave known as the "fourth Industrial Revolution" or "Industry 4.0".
This series of sharing will start from different dimensions such as strategic concept, manufacturing paradigm, promotion strategy, cross-fusion technology, enabling technology, and so on, sort out the evolution of the industry in the past few decades, and make preliminary research and judgment on the current and future trends. It is hoped that through systematic content presentation, business managers, industry practitioners, and readers interested in manufacturing can more comprehensively understand this profound industrial change.
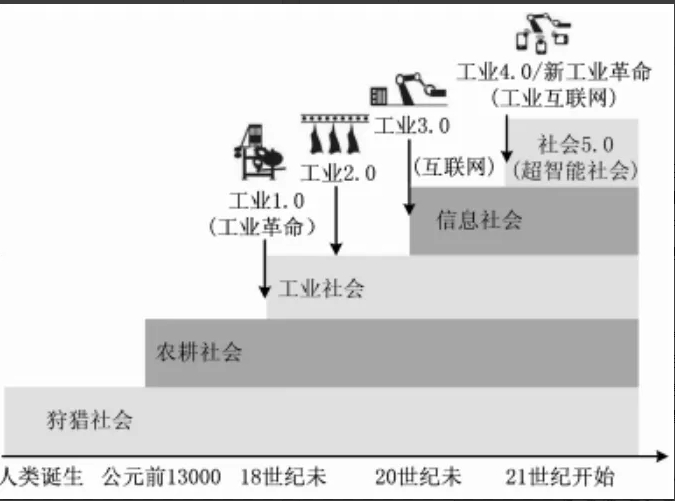
Industrial Revolution and the development of modern society
One hundred years of industrial transformation of the historical wheel
Looking back at the history of world industry, every major revolution not only changed the mode of production, but also changed the face of people's lives.
The first time
The First Industrial Revolution: The rise of the 1760s, marked by the widespread use of steam engines. Previously, manual labor dominated, with low efficiency and low output. After the birth of the steam engine, it provided powerful power for the machine, and mechanized production was opened. The textile industry was the first to change, and machines replaced manual labor, followed by mining, metallurgy, transportation and other industries, and production efficiency was greatly improved, and humans entered the age of steam.
Second time
The Second Industrial Revolution: The 1860s began, with the spread of electricity and mass assembly line production at the center. Electricity injects energy into industry, and lamps, motors and other equipment are wiDeery used to extend production time and provide efficient power. The assembly line moDeercreated by Ford Company standardized and specialized the production process, and the automobile and aircraft industries flourished, greatly changing people's travel and the world.
The third time
The Third Industrial Revolution came in the second half of the 20th century, dominated by computer technology and automated production. Computers are used in all aspects of industrial production to accurately control automation equipment and reduce human error. At the same time, the introduction of information and digital management means, enterprises to achieve real-time monitoring of all links and optimal allocation of resources, electronic information, aerospace, biological engineering and other high-tech industries have risen rapidly.
Industry 4.0
The Fourth Industrial Revolution (Industry 4.0) : The rise of the 21st century, focusing on the Internet of Things, big data, cloud computing, artificial intelligence to empower industry. The Internet of Things enables the interconnection of production equipment and so on to achieve comprehensive perception; Big data collection and analysis of massive production data to help accurate decision-making; Cloud computing provides powerful computing and storage capabilities; Artificial intelligence promotes the application of intelligent robots, warehousing and logistics systems, and the manufacturing mo Deer is "intelligent", and the production is more intelligent, personalized and customized.
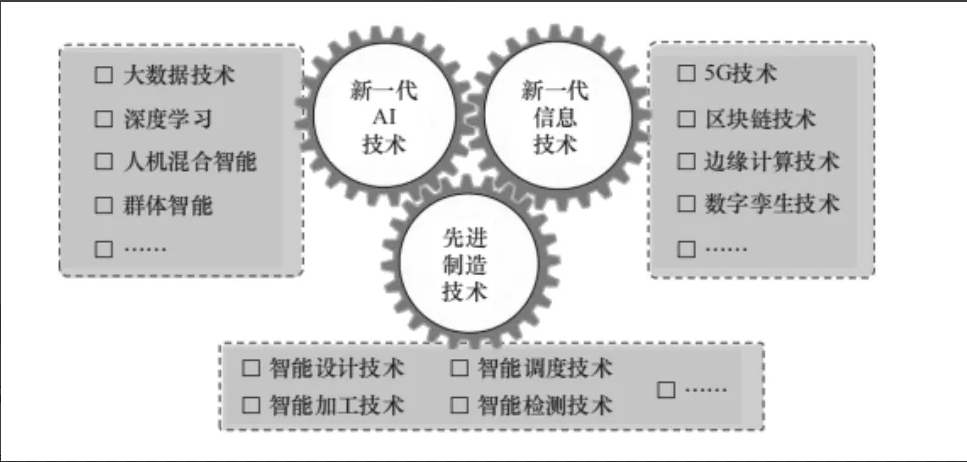
At the same time, the way industries interact continues to evolve: companies and customers, supply chains, and external ecosystems are all interconnected, and traditional industrial "boundaries" are broken. Of course, this is inseparable from the globalization development at the macro level, and it is also inseparable from the information and network support at the micro level. From the perspective of enterprises, the proposal of a series of concepts such as "integration of the two" and "industrial Internet" has made people pay more attention to the collaboration of production factors and the value mining of data.
Focus on digital and intelligent transformation?
Market and policy drive
Consumption upgrading and personalized needs make "flexible manufacturing" possible, and enterprises need to meet customer needs in a more agile and low-cost way. At the same time, countries are also promoting the transformation of industrial structure at the policy level and encouraging the deep integration of manufacturing and information technology to enhance the overall competitiveness.
Technology iteration and cost reduction
Key technologies, including cloud computing, sensors, robots, 5G, etc., continue to mature, the cost continues to decrease, and the application threshold is reduced, so that small and medium-sized enterprises can gradually enjoy the dividends brought by digitalization and intelligence.
Reshaping global supply chains
Affected by multiple factors such as the pandemic and geopolitics, the global supply chain has undergone profound changes. In order to enhance the resilience and risk resistance of the supply chain, manufacturing enterprises have increased the construction of information and intelligent platforms to improve the ability of prediction and collaboration. Therefore, digitalization and intelligence are not just a technological upgrade, but comprehensive changes involving enterprise management, business processes, organizational structure and other aspects, and even affect all aspects of corporate culture and talent training.
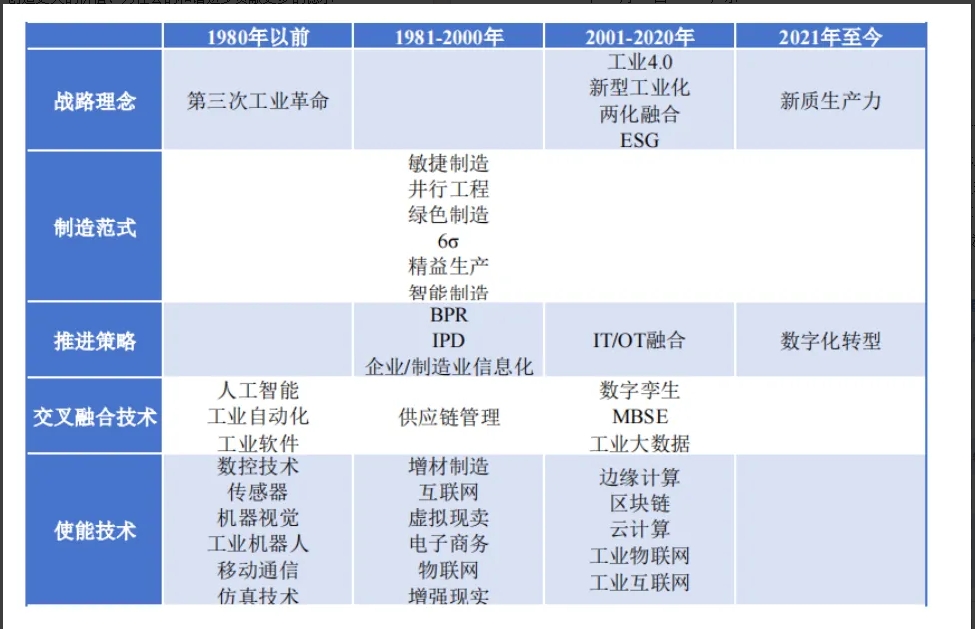
How to make sense of this "timeline" picture?
In the framework of this series of articles, we present a timeline-based "Industrial/manufacturing evolution map" from pre-1980 to 2021 and beyond, stratifying strategic concepts, manufacturing paradigms, propulsion strategies, cross-converging technologies, and enabling technologies at different times. The significance of this graph is:
Vertical dimension: grasp the development stage
Let's see clearly: From the earliest concept of the Third Industrial Revolution and CIMS (Computer Integrated Manufacturing System), to parallel engineering, lean production, agile manufacturing in 1981-2000, to the integration of the two in 2001-2020, Industry 4.0, digital transformation, and finally to the cutting-edge concept of "new quality productivity" after 2021, Each stage of industrial manufacturing has different "keywords".
Horizontal dimension: Insight into the integration of technology and management style
Over time, concepts such as enterprise informatization, BPR (business process reengineering), IPD (Integrated product development), and IT/OT integration have gradually improved. Artificial intelligence, supply chain management, digital twin, MBSE (moDeer-based systems engineering) and other "interdisciplinary" means emerge in an endless stream, while the underlying cloud computing, edge computing, industrial Internet, blockchain and other enabling technologies are constantly updated and iterated. This shows that the manufacturing industry should not only focus on the "production line" itself, but also build new competitive advantages from the perspective of management process, data analysis, and ecological collaboration.
The context of the series of articles and reading prospects?
To help readers better understand this complex picture, we will present 12 popular science articles, each focusing on:
Historical background and conceptual changes: Review the macro strategies and new concepts of each period before 1980, 1981-2000, 2001-2020, and 2021. Manufacturing Paradigm and Advancement Strategy: From CIMS, lean manufacturing, parallel engineering, etc., to intelligent manufacturing, digital transformation, and the integration of BPR, IPD, and IT/OT. Key convergence technology and enabling technology: artificial intelligence, supply chain management, digital twin, industrial big data, edge computing, industrial Internet, etc., the specific value and case in the enterprise landing.
We hope that through the systematic arrangement of these contents, we can provide readers with the following gains:
Clearer industrial thinking: Help enterprise managers or practitioners to clarify the context of technical concepts and management methods, as well as the logical relationship between them. Enlightenment of practical landing: In the subsequent article, we will share some cases or thoughts to provide reference for digital and intelligent landing. Inspired by future trends: macro issues such as new quality productivity and ESG, to the outbreak of underlying enabling technologies, a new round of industrial change is already on the way. This series will also explore some possible future directions in light of industry trends.
Conclusion
The evolution of industry and manufacturing has never stopped, from pure mechanization to the new industrial era dominated by digital twins, and many forces such as technological innovation, business moDeeriteration, and industrial policy promotion are constantly intertwined. For enterprises, understanding the historical context helps to better grasp the current opportunities, and insight into future trends can bring more forward-looking layout inspiration. In the next 11 articles, we will continue to focus on this timeline, in-depth interpretation of strategic concepts, manufacturing paradigms and core technologies at each stage, and combined with typical cases or application scenarios, to present a more three-dimensional picture of the industrial world for readers. I hope this set of content can become a strong support for your thinking and practice of digital and intelligent transformation, and look forward to discussing and witnessing the wonderful future of manufacturing industry with you in reading and sharing.
Abbreviated list
1. CIMS: Computer Integrated Manufacturing System. 2. BPR: Business Process Reengineering. 3. IPD: Integrated Product Development. 4. IT/OT: Information Technology/Operational Technology, the integration of information technology and operational technology. 5. MBSE: MoDeer-Based Systems Engineering. 6. ESG: Environmental, Social, and Governance. 7.5G: Fifth-Generation Mobile Network.


